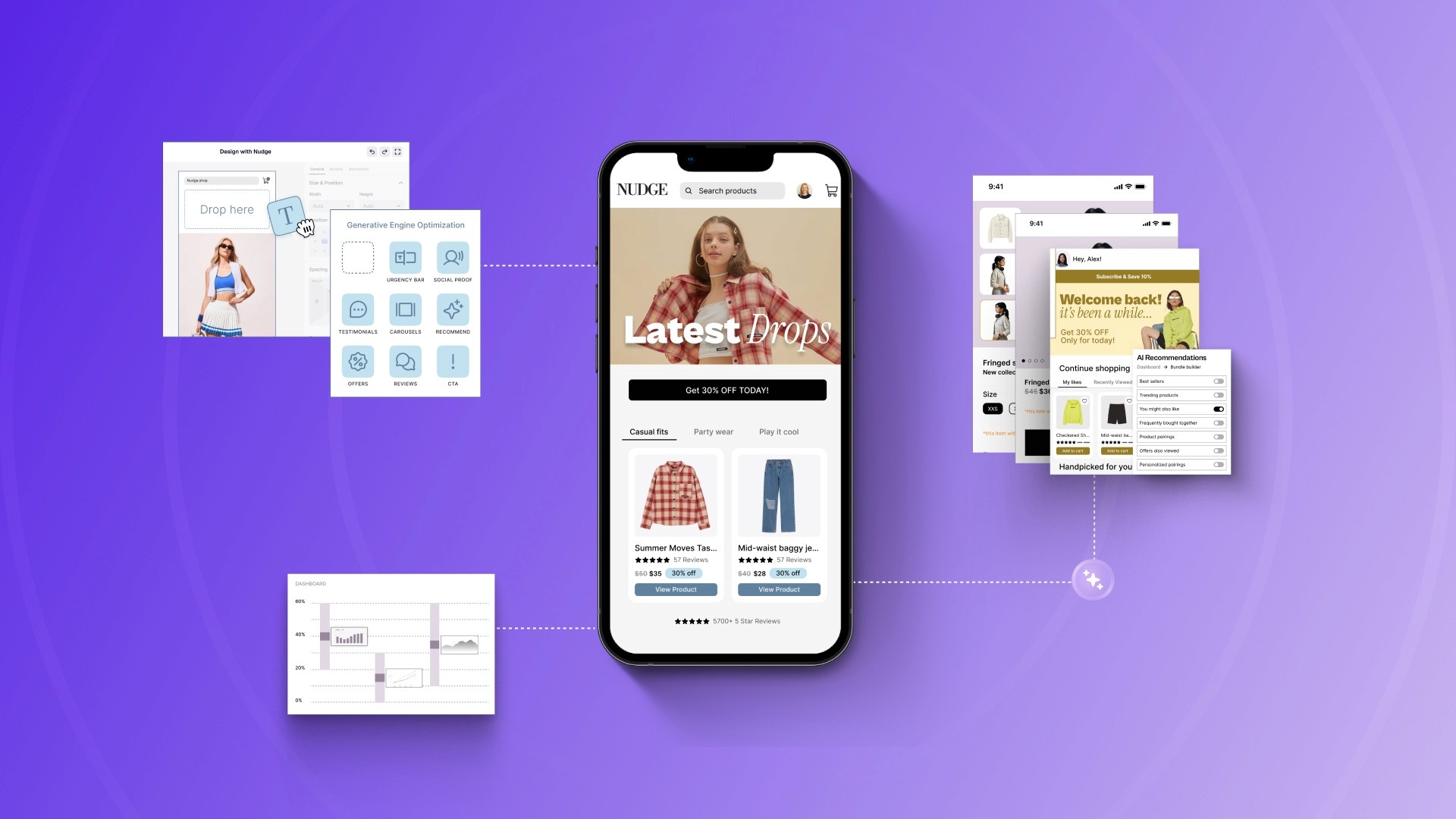
AEO & GEO
The 2026 Guide to Generative Engine Optimization for Ecommerce Teams
Struggling to appear in AI shopping results? Learn how Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) helps ecommerce brands drive discovery and conversions.

Sakshi Gupta
Jan 9, 2026
Shopping has changed a lot in the last few years. People no longer just scroll through websites or search engines and click on ten blue links to find a product. They expect answers to be fast, clear, and relevant. Technology is making this possible, especially with AI.
Today, around one in five Americans use AI platforms to search for products while shopping. They ask questions, compare options, and often make decisions based on the AI suggestions before even visiting a website. This shift means ecommerce brands can no longer rely only on traditional SEO.
In this blog, we will discuss what Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) is and why it matters for ecommerce. We will also discuss how brands can use it to appear in AI-driven shopping answers.
In a nutshell:
Products surface in AI-generated answers only when content is structured, clear, and aligned with shopper intent. GEO emphasizes real-time product relevance over traditional SEO rankings.
Ecommerce teams must optimize landing pages, PDPs, SKU collections, and content clusters for discovery, comparison, and purchase. This ensures consistent structured data, schema, and entity signals across platforms.
Continuous monitoring of AI mentions, assisted conversions, and page-level citations allows iterative improvement and sustained visibility in AI-driven shopping journeys.
Benefit-focused product pages, intent-aligned clusters, and cross-platform consistency help brands dominate generative discovery.
Avoiding common GEO mistakes: overproducing blogs, ignoring schema, or treating GEO like SEO, keeps products included in AI recommendations.
Why Does GEO Matter for Ecommerce (Not Just “Search”)?
Search behavior has changed faster than most ecommerce teams realize. Shoppers ask, compare, and decide inside AI interfaces that summarize options, recommend products, and filter choices before a click ever happens. This shift changes how visibility works, and it fundamentally alters how ecommerce brands compete. Here are various reasons why GEO matters:
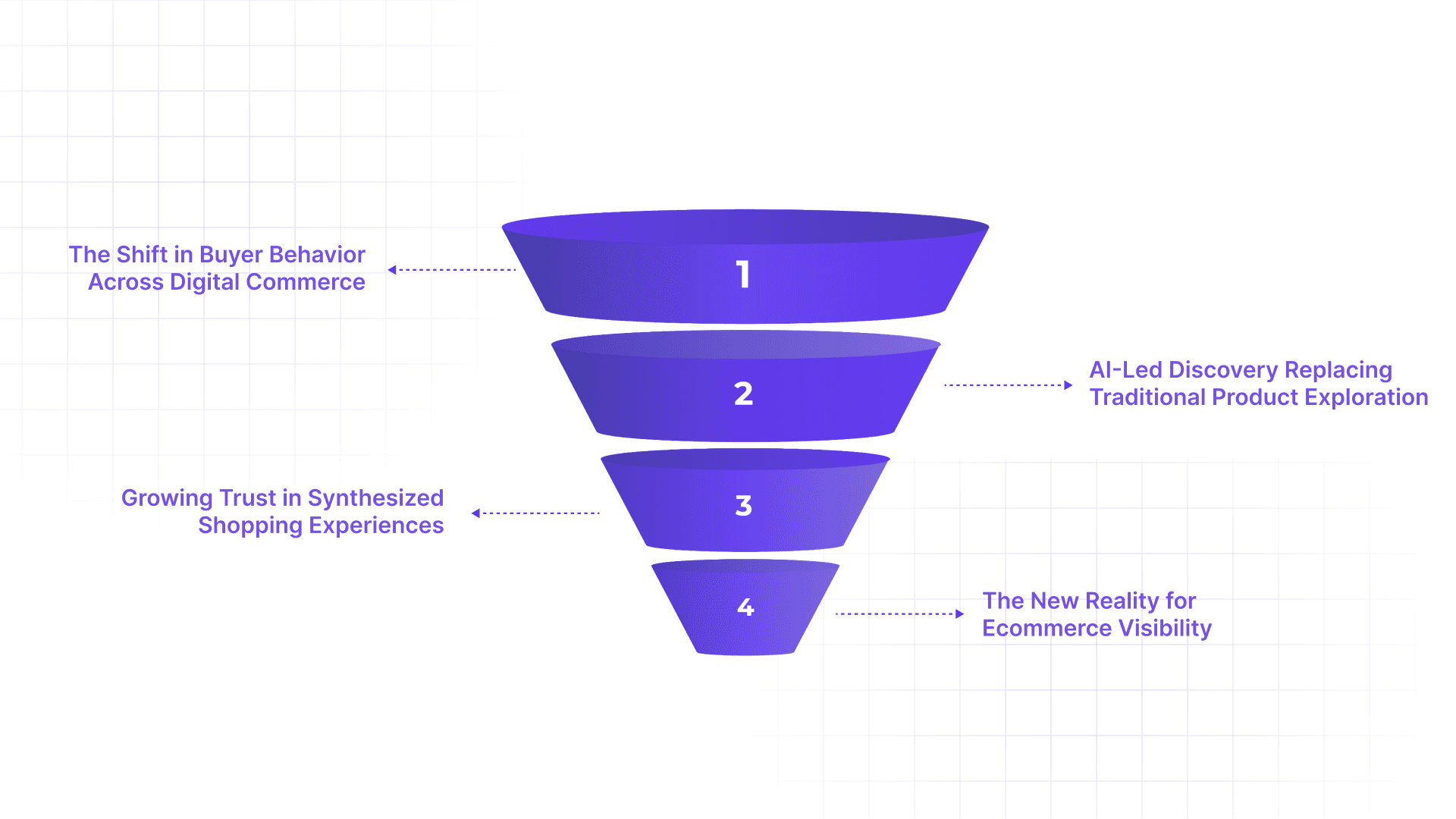
1. The Shift in Buyer Behavior Across Digital Commerce
Buyers are no longer browsing endlessly. They ask direct questions like “Which running shoes are best for flat feet?” or “What’s the best protein powder for beginners?” and expect a single, confident answer. AI engines respond with synthesized guidance pulled from multiple sources, not ranked lists. If your product or brand isn’t part of that synthesis, you’re invisible, even if your SEO rankings look fine.
2. AI-Led Discovery Replacing Traditional Product Exploration
Instead of sending users to ten product pages, generative systems summarize options, compare features, and recommend choices. This compresses the decision journey. Discovery, evaluation, and trust-building now happen in one response. Ecommerce brands must earn presence inside those answers, not just clicks after them.
3. Growing Trust in Synthesized Shopping Experiences
41% of consumers say they trust generative AI search results more than paid search ads. AI-generated answers feel neutral, curated, and efficient, shifting influence away from who ranks first toward who provides the clearest, most reliable product information.
4. The New Reality for Ecommerce Visibility
Visibility is no longer about traffic volume. It’s about being selected when AI compiles its answer. GEO exists to help brands shape how they appear inside those answers before the shopper ever lands on a site.
This shift is rooted in how modern AI systems process information and surface results. To adapt effectively, ecommerce teams need to understand how these engines work beneath the surface.

The Role of Generative Engines in Ecommerce Decision-Making
Generative engines don’t browse ecommerce sites the way humans do. This section breaks down how generative engines interpret ecommerce data, decide what’s relevant, and determine which products surface in AI-generated recommendations.
Foundation Models vs Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG)
Foundation models don’t memorize individual products. Instead, generative systems use retrieval to pull live, structured information when answering a query. If product data isn’t clearly organized or accessible, it simply won’t surface, no matter how well-written it is.
What AI engines actually look for in ecommerce content
Generative systems look for clarity, not creativity. They prioritize:
Structured product attributes
Clear use cases and benefits
Consistent details across pages
If information requires interpretation, AI skips it.
Where ecommerce brands win or lose visibility
Brands gain visibility when product content is clean, consistent, and easy to interpret. They lose it when pages are overloaded with marketing language and light on usable information. In AI-led discovery, structure, not storytelling, determines visibility.
With a clear view of how generative systems work, we can now compare GEO and SEO to understand what actually changes for ecommerce teams in practice.
Also Read: 10 Proven Tactics to Boost AI Search Visibility in 2026
GEO vs SEO: What Changes for Ecommerce Teams
Generative Engine Optimization reshapes ecommerce strategy, shifting focus from ranking pages to influencing AI-driven shopping decisions. Unlike SEO, GEO prioritizes relevance, intent alignment, and structured content that AI can extract. Here’s a clear difference between the two:
Aspect | Traditional SEO | GEO for Ecommerce |
Goal | Improve ranking on search engine result pages | Secure inclusion in AI-generated answers that influence shopper decisions before clicks |
Focus | Single keywords targeting broad search queries | Intent clusters spanning research, comparison, and purchase stages to match real shopper behavior |
Success Metric | Traffic, impressions, keyword positions | Assisted conversions, influence on mid- and bottom-funnel decisions, visibility in AI outputs |
Content | Long-form, generic pages, blog posts | Structured product pages, collections, FAQs, and scannable content designed for AI readability |
Optimization Approach | Periodic updates and A/B testing | Continuous, iterative adaptation to AI query patterns, inventory changes, and shopper intent |
Data Requirements | Standard SEO metadata, occasional schema | Complete, consistent product attributes, trust signals, pricing, availability, and entity reinforcement |
Visibility Strategy | Organic ranking and backlink building | Structured content, authoritative mentions, and AI-understandable signals to surface in responses |
With GEO fundamentally shifting how products are discovered, ecommerce teams need a structured approach to implement, optimize, and measure AI-driven visibility. The next section lays out a complete end-to-end framework for success.
A Step-by-Step Framework for Ecommerce GEO
Generative Engine Optimization requires a structured, end-to-end approach for ecommerce brands. Each phase here focuses on aligning product pages, collections, catalogs, and buyer experiences with how AI interprets and surfaces ecommerce content. Below, we will discuss the various phases of Ecommerce GEO:
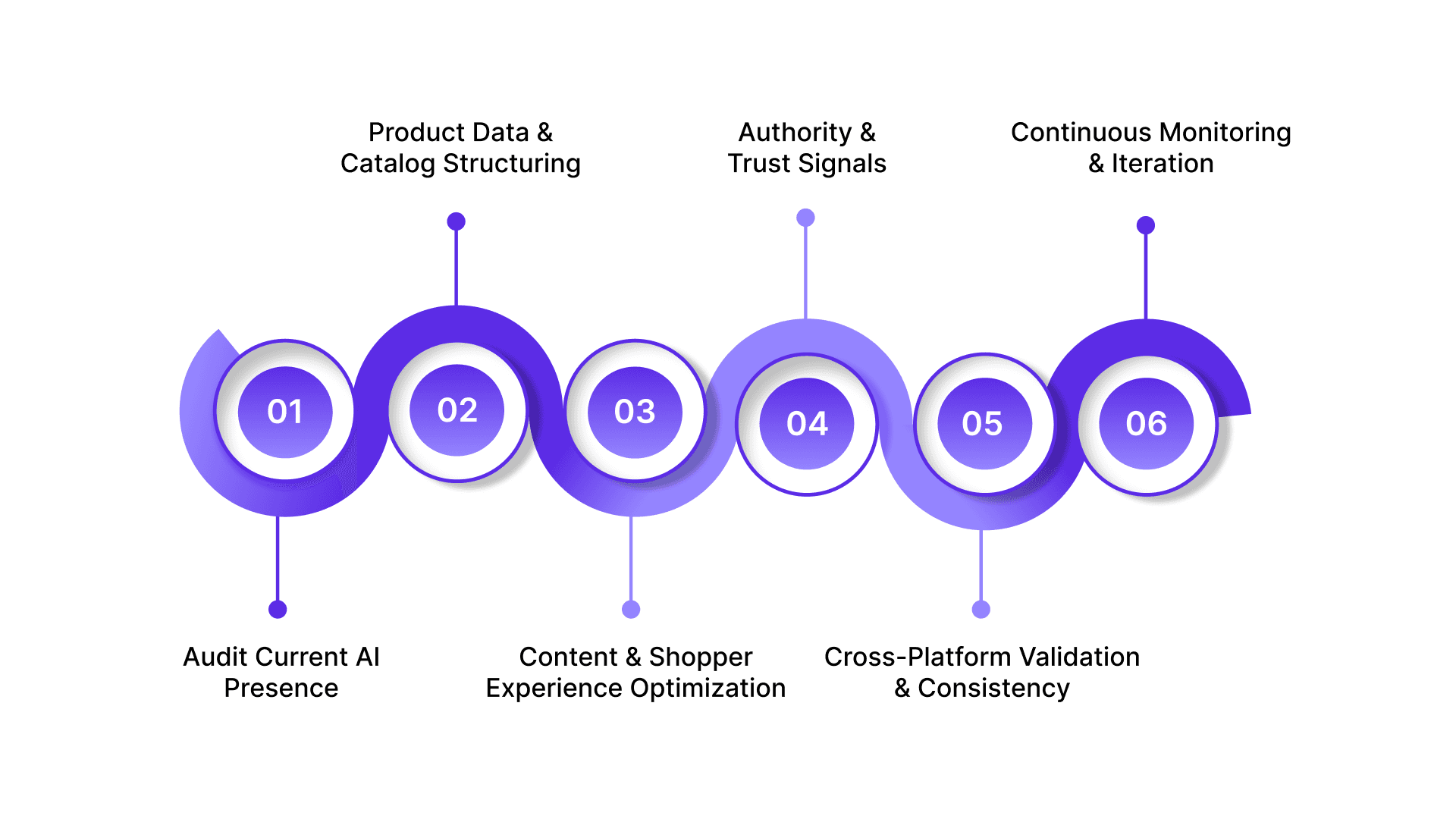
Phase 1: Audit Current AI Presence
Start with mapping where your products appear in AI-generated responses across PDPs, PLPs, and category pages. Identify queries where competitors have surfaced, but your SKUs are missing. Prioritize opportunities based on discovery, comparison, and purchase intent, including high-value categories or bundles.
Phase 2: Product Data & Catalog Structuring
Ensure every product page includes SKU, dimensions, materials, pricing, stock availability, reviews, and variant details. Maintain consistent naming conventions and entity signals across your CMS, feeds, and marketplaces. Structured, retrievable data ensures AI can pull your products into answers.
Phase 3: Content & Shopper Experience Optimization
Replace generic product descriptions with benefit-led copy, scannable FAQs, and real shopper language. Collection and category pages should guide buying decisions, compare alternatives, and answer intent-driven queries, not just list SKUs. Use terminology shoppers actually search for, including category-specific synonyms and long-tail purchase phrases.
Phase 4: Authority & Trust Signals
Reinforce credibility with accurate specs, consistent pricing logic, and verifiable brand mentions across PDPs and collections. Use third-party reviews, marketplace citations, and structured schema to signal reliability. AI systems favor brands with stable, trustworthy, and verifiable product information.
Phase 5: Cross-Platform Validation & Consistency
Extend GEO efforts across marketplaces, social commerce platforms, and review aggregators. Ensure product names, pricing, descriptions, and availability are aligned everywhere. AI engines reference multiple sources, so consistent data across platforms strengthens your inclusion in responses.
Phase 6: Continuous Monitoring & Iteration
Track which PDPs, collections, and category pages appear in AI-generated answers. Monitor assisted conversions, add-to-cart lift, and AOV impact. Refresh high-performing content based on emerging queries, seasonal trends, and inventory shifts. GEO is a continuous optimization layer, not a one-time campaign.
With a structured framework in place, ecommerce teams can move beyond theory and implement actionable tactics that directly influence AI-driven discovery and purchase decisions. The next section dives into GEO tactics that actually move the needle.
5 GEO Tactics That Work for Ecommerce GEO
To win in AI-driven ecommerce discovery, it’s not enough to “publish content.” Brands need tactics that ensure products are surfaced, considered, and purchased. Below are practical strategies designed for high-growth ecommerce teams.
1. Structure Product & Category Page Retrieval
Product and category pages should be built for machine readability, not just visual appeal. Ensure every page includes clearly defined attributes such as size, material, compatibility, and use case.
Category pages should guide decision-making through comparisons, filters, and grouped use cases, making it easier for generative systems to surface the right product at the right moment.
2. Map Content to Buyer Intent
Organize content around how shoppers actually search and decide. This includes:
Discovery: “Best protein powders for beginners.”
Comparison: “Whey vs plant-based protein for recover.y”
Purchase: “Top-rated protein powders under $50.”
Supporting these with FAQs, comparison tables, and buying guides helps AI match your products to real-world questions.
3. Strengthen Entity & Schema Optimization
Consistent structured data is critical for AI retrieval. Apply product, FAQ, and organization schema across all key pages.
Ensure naming conventions, attributes, pricing, and availability match across CMS, feeds, and marketplaces so AI systems can confidently connect references back to your brand.
4. Keep Content Fresh Without Full Rewrites
Instead of rewriting entire pages, make targeted updates: refresh pricing, update availability, rotate featured SKUs, and adjust collections based on seasonality or demand.
These small changes signal relevance and help maintain visibility without constant content overhauls.
5. Optimize Based on AI-Led Performance Signals
Track which pages appear in AI-generated results and how they influence conversions, AOV, and assisted revenue. Use these insights to refine product groupings, page structure, and messaging over time.
AEO isn’t a one-time fix; it’s an ongoing optimization loop driven by real usage signals.
Implementing these tactics ensures your products are visible and influential in AI-driven shopping journeys. The next step is tracking impact; understanding how to measure GEO performance to optimize for conversions and visibility.
Create shoppable funnels that are mapped to prompt-level queries.
How to Measure GEO Performance?
Tracking GEO performance goes beyond traditional SEO metrics. The right metrics show which products, pages, and content structures actually get surfaced, guide buyers, and drive revenue. Here’s how to measure GEO performance:
AI Answer Mentions: Track which products or pages appear in generative responses across platforms. This shows whether your content is being considered in AI-driven discovery.
Assisted Conversions: Measure purchases influenced by AI-discovered products, not just last-click sales. GEO often impacts early-stage decision-making.
Add-to-Cart Lift: Monitor increases in cart activity from AI-surfaced pages to evaluate which content drives action.
Average Order Value Impact: Evaluate how AI-guided recommendations and bundle suggestions influence overall order size.
Page-Level Citations: Identify which PDPs, collections, and guides are frequently referenced by AI, highlighting content formats and structures that work.
Schema & Entity Effectiveness: Track how structured data and consistent product/entity signals contribute to visibility and retrieval across generative engines.
Nonetheless, even with the right framework and measurement in place, ecommerce brands often stumble on avoidable errors. Understanding these pitfalls is important; next, we highlight common GEO mistakes and how to prevent them.
Common GEO Mistakes Ecommerce Brands Make
Even experienced ecommerce teams often misapply GEO, sticking to old SEO habits or focusing on content volume instead of driving product-level impact. The errors mentioned below can remove your products from AI-driven recommendations, lowering visibility, assisted conversions, and revenue.
1. Treating GEO as a Keyword Exercise
Unlike traditional SEO, GEO isn’t about ranking for isolated keywords. AI evaluates structured product attributes, PDP content, category pages, and entity signals. Focusing solely on keywords risks your product pages, collections, and bundles being ignored in generative answers.
2. Publishing Content Without Transactional Intent
Generic blogs or guides without clear product relevance fail to surface in AI-driven shopping queries. Every page, PDPs, PLPs, collection pages, and buying guides should support discovery, comparison, or purchase decisions, guiding shoppers toward conversion.
3. Ignoring Structured Data and Product Schema
AI engines prioritize structured attributes, product schema, FAQ schema, and organization schema. Skipping schema or inconsistently labeling SKUs, pricing, availability, product variants, and collections prevents AI from reliably surfacing your products, even if traditional search rankings look strong.
4. Overproducing Blogs While Under-Optimizing PDPs and Collections
Many brands focus on content volume instead of optimizing PDPs, PLPs, and collection pages that influence revenue. AI favors structured, scannable product content with clear benefits, comparisons, and use cases over generic thought leadership.
5. Lack of Continuous Monitoring and Iteration
GEO is a continuous optimization layer. Failing to track AI mentions, PDP and PLP visibility, assisted conversions, bundle performance, and emerging product queries allows competitors to dominate high-intent categories. Regular monitoring ensures products remain visible and conversion-ready.
Avoiding common GEO mistakes ensures your products remain visible and influential in AI-driven shopping journeys. Next, we look ahead at how the future of GEO will reshape ecommerce, from dynamic storefronts to continuous optimization.
The Future of GEO for Ecommerce Brands
Shopping is shifting from traditional browsing to AI-driven recommendations. Generative engines will assemble dynamic storefronts tailored to each shopper’s context, ad source, location, and past behavior, rather than relying on fixed navigation or static pages.
Brands that structure product data, PDPs, PLPs, and collections for AI retrieval, not just human readability, will dominate visibility and influence purchase decisions.
GEO is no longer a one-time campaign; it’s a continuous operating layer connecting your product catalog to customer journeys, driving discovery, conversions, and long-term revenue growth.
Also Read: 9 Top AI Search Visibility Tools to Boost Rankings in 2026
How Nudge Helps Ecommerce Brands Excel with GEO
For high-growth ecommerce brands, Nudge helps products surface in AI-driven shopping responses, influencing discovery, comparison, and purchase decisions. Unlike generic tools, Nudge focuses on structured product data, real-time relevance, and AI retrieval, ensuring PDPs, PLPs, and collection pages are correctly represented in generative answers.
Nudge’s key capabilities include:
AI Search Visibility: Understand where your brand appears in AI answers, how models position you, and which prompts or categories present the biggest visibility gaps and opportunities.
Shoppable Funnels: Generate shoppable funnels based on the exact prompt that drove the visit, helping shoppers move confidently from answer to checkout.
Product Experiences: Dynamically build personalized interfaces like full pages and UX components that adapt contextually to real-time data.
Continuous Monitoring: Measure AI mentions, visibility shifts, and emerging queries for ongoing optimization.
With Nudge, ecommerce brands maintain visibility, credibility, and influence in AI-powered discovery.

Conclusion
Generative Engine Optimization is reshaping how shoppers discover and purchase products. In AI-driven shopping, visibility no longer depends on ranking alone. Structured product data, intent-aligned content, and clear entity signals determine which PDPs, collections, and bundles appear in AI-generated answers. Ecommerce brands that optimize for AI inclusion influence decisions at every stage, from discovery to checkout, ensuring products are considered even before users click.
Nudge enables brands to execute GEO effectively, providing real-time product relevance, structured data management, and dynamic personalization across PDPs, PLPs, and collections. Features like AI Search Visibility, Shoppable Funnels, Product Experiences, and Continuous Monitoring help brands maintain a consistent presence, credibility, and influence in AI-powered discovery.
Book a demo to see how Nudge ensures your PDPs, PLPs, and collections appear in AI-driven answers, boosting visibility, conversions, and ecommerce revenue.
FAQs
1. How long does GEO take to work?
For ecommerce brands, the GEO impact varies by catalog size, product data quality, and update frequency. Small catalogs see AI visibility in 4-6 weeks, while larger stores may require 8-12 weeks of structured optimization and monitoring.
2. Can small businesses benefit from GEO?
Absolutely. Niche ecommerce stores gain AI-driven visibility by structuring product attributes, collections, and buying-intent content. Targeted, highly specific offerings can appear in generative answers, enabling small brands to compete with larger retailers without massive traffic or budgets.
3. How do I track AI citations?
Track mentions by monitoring AI chat interfaces, voice assistants, and generative platforms. Measure which PDPs, collections, and bundles are cited, how frequently, and in what context. Structured data reporting and cross-platform analytics ensure continuous visibility optimization.
4. Which platform should I optimize for first?
Prioritize the platform generating the highest discovery potential. ChatGPT might surface bundles and FAQs, while Google’s AI recommends top products. Analyze competitor dominance, current visibility, and shopper behavior to determine the platform that maximizes early AI-driven conversions.